

Synchronization is the most popular form of cloud storage.
Except in IT professional environments, cloud storage means synchronization for almost everyone.
It is the operating mechanism of all systems called Virtual Disks.
Some examples would be the following, some are US and some are European products.
Once the software is installed, there will always be one or more folders that you select on your computer. The application will act on these folders.
The idea is that the designated files and folders remain in the cloud. They are saved, and identical copies are kept on both sides.

The end result should always be having the same folder structure, with all your files, both locally and in the Cloud.
Synchronization is an Algorithm, an automated process that can have many variants in the way it acts. But in all cases it acts as follows:
The synchronization process depends on a time and a state of affairs.
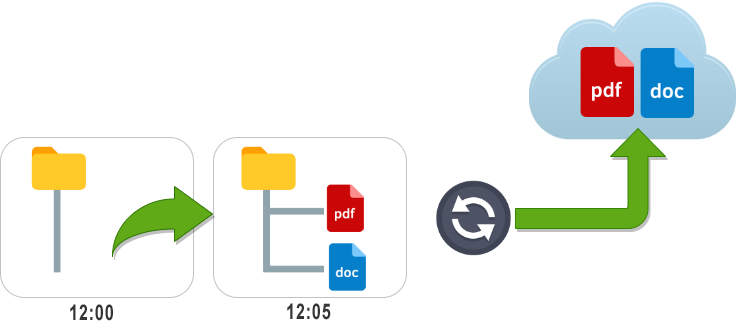
At one time, for example at 12:00 am, there is a folder that is empty. At another time, 12:05 am, the folder contains two files.
The detection of this change of state of the folder causes: internally, without us seeing anything on the screen, the software will send these two files to the Cloud.
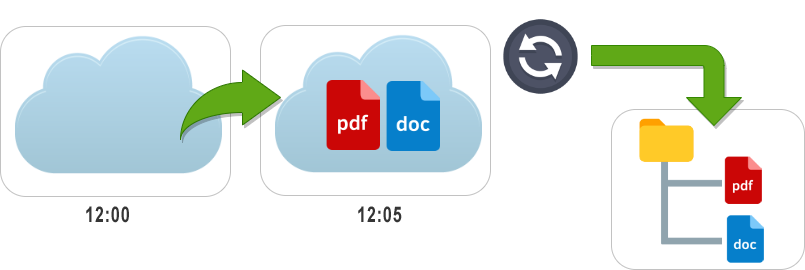
There is also a change detected in the other way. There are files in the cloud that are missing from our local folder.
After detecting this situation, the virtual disk, i.e. the synchronizer, downloads the files to the corresponding folder. The software does this in a hidden way, on our computer we will see that these files appear in the folder.
So far we have seen two simple cases. When the files do not exist on either side.
Now a problem arises.
We are all used to working with files that reside in our local folders. There, we are free to modify the files. We can replace, edit or delete them.
If we delete, it's also simple, the program will detect that we have deleted locally and it will delete it from the Cloud. On the contrary, if it is in the cloud, it is synchronized and deleted from our local folder.
But, if we change or modify a file locally and there is already a copy of the same file in the cloud, we have a problem.
Let's imagine a situation we could face. If we have modified the files in our local folder, we can consider two situations:
In these cases, as long as there is only one person using the synchronization, the solution is simple. The system will replace the files with their most recent versions.
If another person synchronizes the folders at the same time, the problem is difficult to solve. This is an inherent problem with synchronizers.
With only two people using the system, we can have three versions of the same file:
Which version is the correct one and which one should be uploaded to the Cloud?
John will say that he has spent hours working on the file and it should be the good version, Peter will say the same.
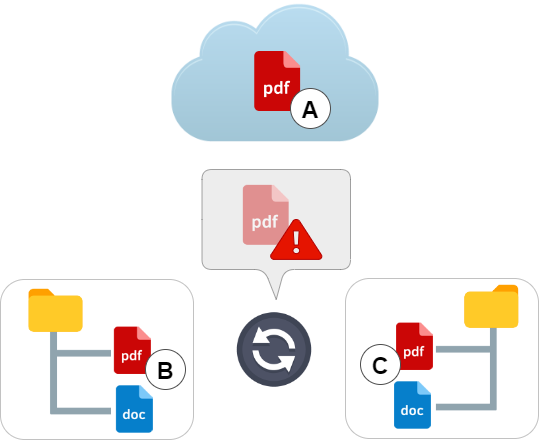
In the end this problem has to be solved manually.
It will be necessary to indicate which copy is considered to be the correct one.
The first thing to say is that synchronization, and basically the invention of the virtual disk, corresponds to the goal of making files available to a single individual at any time and any place.
Virtual disks are a very good way for a single person to keep their files stored in one place. Files are made available by accessing them from any device, be it a computer, a tablet or a mobile phone.
We will see below the reasons why synchronization is not suitable for a company or a group of users.
The disadvantages of synchronization in general are as follows:
At a personal level we only need to make sure that the provider maintains the appropriate security measures. We can use it to store family photos or any of our documents. We do not want that there is data exposed to theft by the provider company or by third parties.
In this case, the level of protection depends on the provider.
At a business level, things change a lot, since every company keeps files with confidential customer data. A simple invoice is already subject to appropriate data protection.
Synchronization keeps as many copies of the files on as many devices as we use. If there are several employees in the company, there will be many more copies of the files on many more devices. If any of those files can be seen or stolen by third parties, we have a privacy or data protection problem.

There have always been different ways and applications available for cloud storage.
For more than a decade, the system used was the well-known FTP (File Transfer Protocol). We had a server to which we connected via an FTP client application.
Computer professionals and programmers still generally use this method.
Companies also used broadly another method called corporate intranets. They were a type of web page where files were uploaded to be saved, and made available to other users.
These media were not as immediate or as convenient as a Virtual Disk, which may be why its use has become so popular.
Nowadays, Cloud Computing provides us with other means.
Surprising as it may seem, we can have a mapped drive in the cloud.
A mapped drive is nothing more than a disk on our computer to which we assign a drive letter. We can have a drive called ‘Z:’ on our PC but it is actually in the Cloud.
This allows us to connect to that disk from any computer and even have several users using it at the same time.
The best example of this type of solution is MapDrive by Dataprius. It is a solution whose concept and innovation has led Dataprius to be rated as one of the 64 most innovative companies in Cloud Computing, according to the British press.
The best example of an Intranet for storing and working daily with files in the Cloud without the need for synchronisation is of course Dataprius.